Services

Hypertension
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is when the force of blood against artery walls is too high, often without symptoms. It increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. Key factors include genetics, poor diet, lack of exercise, and stress. Regular check-ups, a healthy diet, exercise, and medication can help manage it. Seek medical advice if you experience severe headaches, chest pain, or shortness of breath.

Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart can't pump blood effectively, leading to fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs. Common causes include coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Management includes medications, lifestyle changes like a low-sodium diet, regular exercise, and sometimes surgical interventions. Regular monitoring and medical care are crucial.

Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is an irregular and often rapid heart rate that can cause palpitations, fatigue, and shortness of breath. It increases the risk of stroke and heart failure. Common causes include high blood pressure, heart disease, and thyroid disorders. Management includes medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes procedures to restore normal rhythm. Regular monitoring and medical care are essential. Seek immediate help for severe or sudden symptoms.
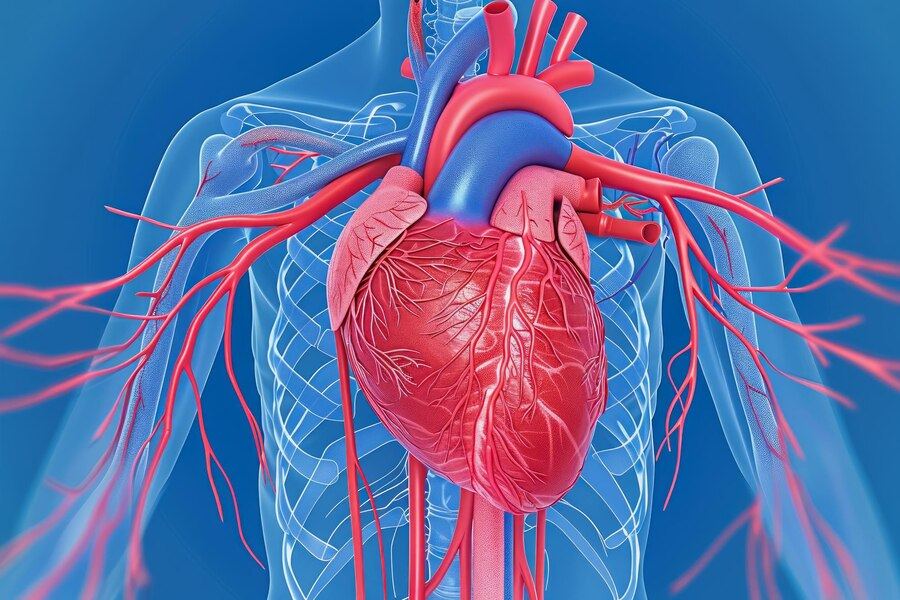
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease (CAD) occurs when the heart's arteries narrow or become blocked, reducing blood flow. This can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and heart attacks. Major risk factors include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. Management involves lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgical procedures like angioplasty. Regular check-ups and adhering to treatment plans are crucial. Seek immediate help for severe chest pain or sudden symptoms.
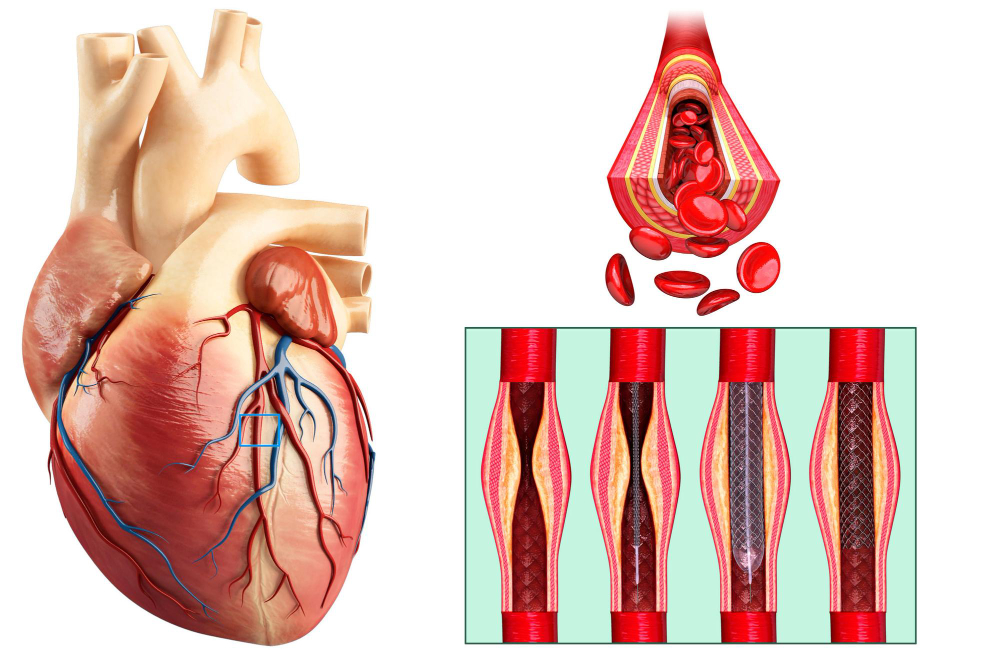
Coronary Angioplasty and Stenting
Coronary angioplasty and stenting are medical procedures used to open narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, improving blood flow to the heart. Angioplasty involves threading a catheter with a small balloon through the artery to the blockage site, where the balloon is inflated to widen the artery. A stent, a small mesh tube, is then placed to keep the artery open. This can relieve symptoms like chest pain and prevent heart attacks. Major risks include bleeding, artery damage, and re-narrowing of the artery.
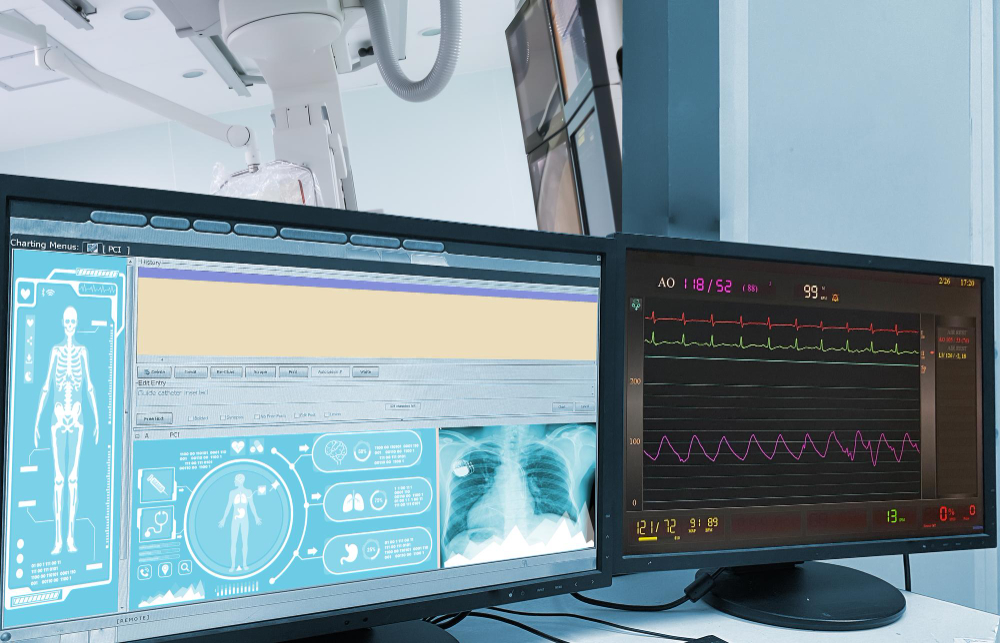

Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
PCI is a non-surgical procedure used to treat narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, which can restore blood flow to the heart muscle. During PCI, a catheter is inserted through the skin into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. A balloon at the catheter's tip is inflated at the site of the blockage to open the artery, and a stent may be placed to keep it open. PCI can relieve symptoms such as chest pain and reduce the risk of heart attacks. Potential risks include bleeding, artery damage, and re-narrowing of the artery.
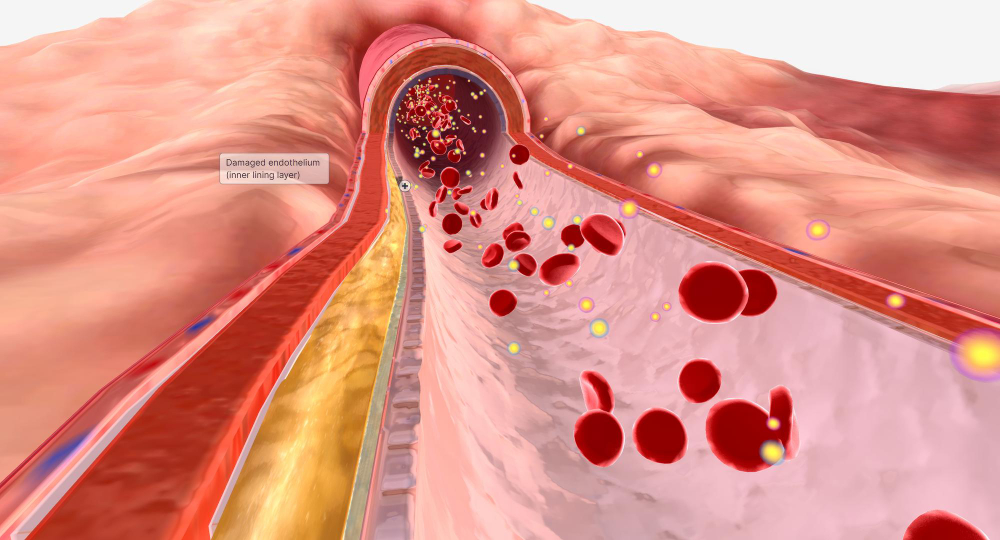
Lipid Disorders
Lipid disorders involve abnormal levels of lipids (fats) in the blood, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, which can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Common lipid disorders include high cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia) and high triglycerides (hypertriglyceridemia). These conditions are often influenced by factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, obesity, genetic predisposition, and other health conditions like diabetes.
Heart Murmurs
Heart murmurs are unusual sounds heard during a heartbeat, often resembling a whooshing or swishing noise, caused by turbulent blood flow through the heart or its valves. Heart murmurs can be classified as innocent or abnormal. Innocent murmurs are common and usually harmless, often found in healthy individuals and do not require treatment.

Congenital Heart Defects
Congenital heart defects (CHDs) are structural abnormalities of the heart present at birth, affecting the heart's walls, valves, or blood vessels. CHDs can range from simple issues that cause no symptoms to complex problems that can cause life-threatening complications. Common types of CHDs include atrial septal defect (ASD), ventricular septal defect (VSD), tetralogy of Fallot, and transposition of the great arteries.
